Power BI in Healthcare: Practical Analytics That Improve Care

Why healthcare analytics trends matter now
Hospitals and clinics generate a constant stream of clinical, operational, and financial data. Acting on that data quickly is essential for patient safety, service quality, and cost control. Static reports delay action, while shared dashboards put everyone on the same page. When clinical leaders, operations, and finance review the same measures inside Microsoft Teams or an internal portal, they coordinate staffing, spot risks earlier, and reduce manual handoffs. Current healthcare analytics trends also show a shift from retrospective views to predictive insight. Risk models flag patients who may be readmitted, outreach teams track results by cohort, and population health metrics guide preventive programs. The central idea is simple. Use timely information in daily workflows so teams make decisions when they matter most.
How Power BI in healthcare supports real-time and predictive decisions
Power BI in healthcare connects to core systems, then presents clear visual analysis that guides both bedside care and hospital command centers. Live pages can show bed status, staffing variance, operating room schedules, vitals, and lab results. If a patient’s markers begin to worsen, a tile can move from green to amber to red. Nurses and physicians see the change in the ward view and act sooner. At a system level, leaders can watch admission surges, bottlenecks, and diversion risk in near real time, then adjust plans before delays grow.
Predictive analytics is the second pillar. Power BI works with Azure Machine Learning so teams can run models on electronic health record history and social factors. Common examples include readmission likelihood, ICU demand during flu season, and medication shortage risk. Department pages then segment cohorts by condition or demographics, show outreach progress, and send alerts when thresholds are crossed. These patterns align with healthcare analytics trends that prize early signals, not just monthly summaries. When the same view is embedded in daily huddles and executive standups, clinical, financial, and operational decisions line up without long email chains or ad-hoc spreadsheets.
Benefits across clinical care, operations, and patient experience
Clinical workflows. Through FHIR connectors, Power BI in healthcare brings referrals, encounters, procedures, results, and billing records into a single model. During urgent events, staff can view history, telemetry, and labs together, which reduces paging and back-and-forth. Teams coordinate faster because everyone is looking at the same context.
Operations. Live dashboards show OR block use, room turnover time, delay causes, bed occupancy by unit, and staffing gaps. Unit managers can reassign shifts, resequencing cases, and prepare discharge tasks based on what the next hours are likely to bring. That limits idle time and last-minute scrambling.
Patient experience. Shared pages track feedback scores, wait time trends, referral turnaround, and complaint resolution. When a service gap appears, owners are clear, and fixes move faster. Reviewing the same small set of metrics each week drives steady gains that patients notice.
Department-focused views. The data model supports tailored pages without breaking enterprise standards. Clinical teams can monitor length of stay, time to antibiotics, and lab turnaround. Finance can compare cost and revenue against volumes by service line. Supply chain can track pharmaceuticals and consumables, including feeds from IoT trackers connected through FHIR APIs in the Microsoft cloud for healthcare. Row-level security limits who can see patient-level records while still allowing comments and co-authoring on shared reports.
Privacy, compliance, and a practical rollout plan
Patient data requires strict protection. Power BI in healthcare runs on Microsoft cloud services that support HIPAA and HITECH requirements and carry ISO 27001 and ISO 27018 certifications. Organizations can sign a Business Associate Agreement. Data is encrypted at rest with customer-managed keys and in transit with TLS 1.2 or higher. Row-level and object-level security restrict access by role and location. Audit logs record views, exports, and shares so compliance teams can trace activity. Azure Active Directory provides single sign-on and multi-factor authentication. Network controls such as private endpoints, Virtual Network integration, and ExpressRoute keep analytics traffic inside approved boundaries.
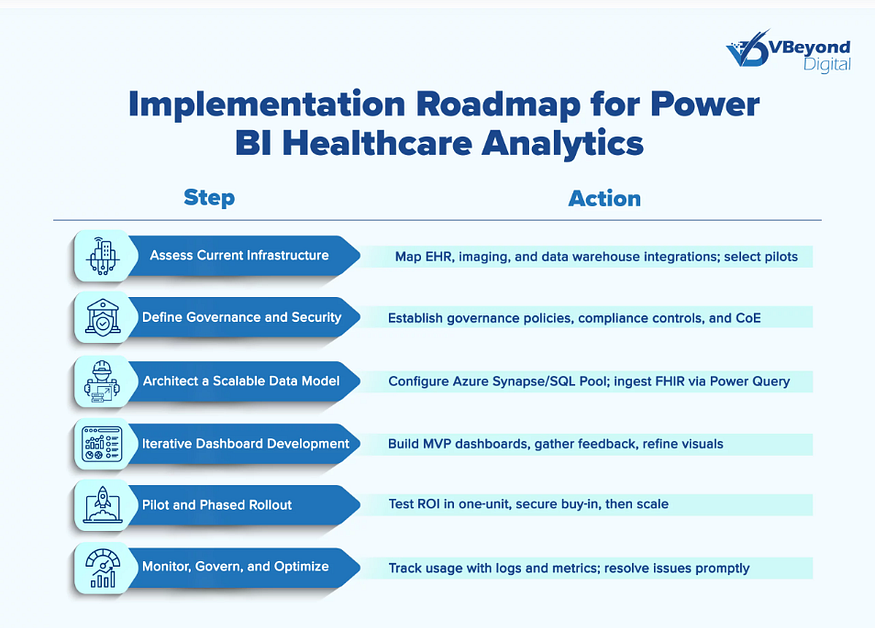
A focused rollout keeps momentum high while reducing risk:
- Assess current systems. List EHR platforms, imaging tools, departmental apps, and any data warehouse. Pick a pilot that matters to patient care and operations, for example emergency department throughput or readmission risk by unit.
- Set governance. Create a BI Center of Excellence that defines metric owners, naming standards, and certified datasets. Publish a simple request path for access and change control. This avoids shadow reporting and confusion about definitions.
- Build the model. Use Azure Synapse or SQL as the semantic layer. Ingest FHIR resources with Power Query. Shape a star schema with facts for Encounters, Orders, Results, and Admissions, plus shared dimensions for Patient, Provider, Location, Diagnosis, and Time. Add row-level security that matches units and service lines.
- Ship MVP dashboards. Release a small set of pages that solve clear problems, such as door to provider time in the ED, readmission risk lists with intervention tracking, and OR block use with turnover time. Put them in front of end users, collect feedback, and revise quickly.
- Pilot, measure, expand. Run the pilot in one department, such as cardiology. Quantify time saved, delays avoided, and key outcome shifts. Use those results to secure support and budget for additional areas.
- Operate and improve. Watch capacity metrics and audit logs, tune refresh schedules, and use aggregations and incremental refresh for performance. Retire duplicate reports and keep a short catalog of certified content. Review alert rules monthly to cut noise and raise signal quality.
Training that sticks.
Analysts need depth in modeling, DAX, and AI visuals. Clinicians benefit from short sessions on reading dashboards during rounds, subscribing to alerts, and adding context through notes. IT and compliance teams should learn workspace governance, security configuration, and monitoring. Hands-on workshops with anonymized visit data let cross-functional groups build a working dashboard tied to real tasks. Encourage the PL 300 certification and hold recurring clinics where teams share what they built and what they learned.
Power BI in healthcare lines up with key healthcare analytics trends by bringing timely insight, prediction, and secure sharing into daily work. Start with one or two high-value scenarios, release early, measure what changes, and grow from there. The payoff is faster decisions, better coordination, and measurable gains in patient care and efficiency.

Comments
Post a Comment